Segmentation
In Operating Systems, Segmentation is a memory management technique in which the memory is divided into the variable size parts. Each part is known as a segment which can be allocated to a process.
The details about each segment are stored in a table called a segment table. Segment table is stored in one (or many) of the segments.
Segment table contains mainly two information about segment:
- Base: It is the base address of the segment
- Limit: It is the length of the segment.
Why Segmentation is required?
Till now, we were using Paging as our main memory management technique. Paging is more close to the Operating system rather than the User. It divides all the processes into the form of pages regardless of the fact that a process can have some relative parts of functions which need to be loaded in the same page.
Operating system doesn't care about the User's view of the process. It may divide the same function into different pages and those pages may or may not be loaded at the same time into the memory. It decreases the efficiency of the system.
It is better to have segmentation which divides the process into the segments. Each segment contains the same type of functions such as the main function can be included in one segment and the library functions can be included in the other segment.
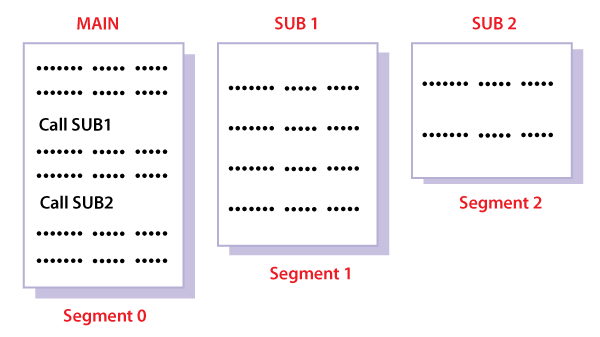
Advantages of Segmentation
- No internal fragmentation
- Average Segment Size is larger than the actual page size.
- Less overhead
- It is easier to relocate segments than entire address space.
- The segment table is of lesser size as compared to the page table in paging.
Disadvantages
- It can have external fragmentation.
- it is difficult to allocate contiguous memory to variable sized partition.
- Costly memory management algorithms.