CPU Scheduling
CPU Scheduling is a process that allows one process to use the CPU while another process is delayed (in standby) due to unavailability of any resources such as I / O etc, thus making full use of the CPU. The purpose of CPU Scheduling is to make the system more efficient, faster, and fairer.

Tutorial on CPU Scheduling Algorithms in Operating System
Whenever the CPU becomes idle, the operating system must select one of the processes in the line ready for launch. The selection process is done by a temporary (CPU) scheduler. The Scheduler selects between memory processes ready to launch and assigns the CPU to one of them.
What is a process?
In computing, a process is the instance of a computer program that is being executed by one or many threads. It contains the program code and its activity. Depending on the operating system (OS), a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions concurrently.
How is process memory used for efficient operation?
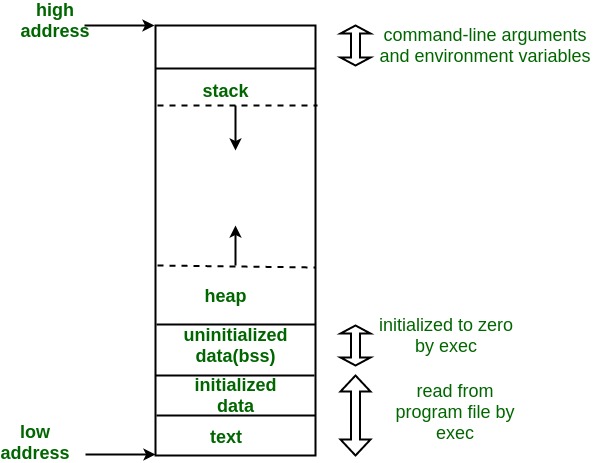
The process memory is divided into four sections for efficient operation:
- The text category is composed of integrated program code, which is read from fixed storage when the program is launched.
- The data class is made up of global and static variables, distributed and executed before the main action.
- Heap is used for flexible, or dynamic memory allocation and is managed by calls to new, delete, malloc, free, etc.
- The stack is used for local variables. The space in the stack is reserved for local variables when it is announced.
To know further, you can refer to our detailed article on States of a Process in Operating system.
What is Process Scheduling?
Process Scheduling is the process of the process manager handling the removal of an active process from the CPU and selecting another process based on a specific strategy.
Process Scheduling is an integral part of Multi-programming applications. Such operating systems allow more than one process to be loaded into usable memory at a time and the loaded shared CPU process uses repetition time.
There are three types of process schedulers:
- Long term or Job Scheduler
- Short term or CPU Scheduler
- Medium-term Scheduler
Why do we need to schedule processes?
- Scheduling is important in many different computer environments. One of the most important areas is scheduling which programs will work on the CPU. This task is handled by the Operating System (OS) of the computer and there are many different ways in which we can choose to configure programs.
- Process Scheduling allows the OS to allocate CPU time for each process. Another important reason to use a process scheduling system is that it keeps the CPU busy at all times. This allows you to get less response time for programs.
- Considering that there may be hundreds of programs that need to work, the OS must launch the program, stop it, switch to another program, etc. The way the OS configures the system to run another in the CPU is called “context switching”. If the OS keeps context-switching programs in and out of the provided CPUs, it can give the user a tricky idea that he or she can run any programs he or she wants to run, all at once.
- So now that we know we can run 1 program at a given CPU, and we know we can change the operating system and remove another one using the context switch, how do we choose which programs we need. run, and with what program?
- That’s where scheduling comes in! First, you determine the metrics, saying something like “the amount of time until the end”. We will define this metric as “the time interval between which a function enters the system until it is completed”. Second, you decide on a metrics that reduces metrics. We want our tasks to end as soon as possible.
What is the need for CPU scheduling algorithm?
CPU scheduling is the process of deciding which process will own the CPU to use while another process is suspended. The main function of the CPU scheduling is to ensure that whenever the CPU remains idle, the OS has at least selected one of the processes available in the ready-to-use line.
In Multiprogramming, if the long-term scheduler selects multiple I / O binding processes then most of the time, the CPU remains an idle. The function of an effective program is to improve resource utilization.
If most operating systems change their status from performance to waiting then there may always be a chance of failure in the system. So in order to minimize this excess, the OS needs to schedule tasks in order to make full use of the CPU and avoid the possibility of deadlock.
Objectives of Process Scheduling Algorithm:
- Utilization of CPU at maximum level. Keep CPU as busy as possible.
- Allocation of CPU should be fair.
- Throughput should be Maximum. i.e. Number of processes that complete their execution per time unit should be maximized.
- Minimum turnaround time, i.e. time taken by a process to finish execution should be the least.
- There should be a minimum waiting time and the process should not starve in the ready queue.
- Minimum response time. It means that the time when a process produces the first response should be as less as possible.
What are the different terminologies to take care of in any CPU Scheduling algorithm?
- Arrival Time: Time at which the process arrives in the ready queue.
- Completion Time: Time at which process completes its execution.
- Burst Time: Time required by a process for CPU execution.
- Turn Around Time: Time Difference between completion time and arrival time.
Turn Around Time = Completion Time – Arrival Time
- Waiting Time(W.T): Time Difference between turn around time and burst time.
Waiting Time = Turn Around Time – Burst Time
Things to take care while designing a CPU Scheduling algorithm?
Different CPU Scheduling algorithms have different structures and the choice of a particular algorithm depends on a variety of factors. Many conditions have been raised to compare CPU scheduling algorithms.
The criteria include the following:
- CPU utilization: The main purpose of any CPU algorithm is to keep the CPU as busy as possible. Theoretically, CPU usage can range from 0 to 100 but in a real-time system, it varies from 40 to 90 percent depending on the system load.
- Throughput: The average CPU performance is the number of processes performed and completed during each unit. This is called throughput. The output may vary depending on the length or duration of the processes.
- Turn round Time: For a particular process, the important conditions are how long it takes to perform that process. The time elapsed from the time of process delivery to the time of completion is known as the conversion time. Conversion time is the amount of time spent waiting for memory access, waiting in line, using CPU, and waiting for I / O.
- Waiting Time: The Scheduling algorithm does not affect the time required to complete the process once it has started performing. It only affects the waiting time of the process i.e. the time spent in the waiting process in the ready queue.
- Response Time: In a collaborative system, turn around time is not the best option. The process may produce something early and continue to computing the new results while the previous results are released to the user. Therefore another method is the time taken in the submission of the application process until the first response is issued. This measure is called response time.